In this Guide we will see on How to Install the Oracle Database 12c Release 2 in Redhat Enterprise Linux 7.5 Server.
To Download the Oracle Database Installer, Visit the below URL:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/database/enterprise-edition/downloads/index.html
The installer will create an Oracle VM VirtualBox group in the Windows Start menu, which enables you to launch the application and access its documentation. With standard settings, Oracle VM VirtualBox will be installed for all users on the local system. If this is not wanted, you must invoke the installer by first extracting as follows. Following, you can find a description of options, or additional features, that are available for Amazon RDS instances running the Oracle DB engine. To enable these options, you add them to an option group, and then associate the option group with your DB instance. Note If you use a third-party Oracle provider, and your Oracle provider cannot run outside a SQL Server process, enable it to run in-process by changing the provider options. To change the provider options, use one of the following methods. Method 1 Locate the following registry key. Then, change the value of the AllowInProcess (DWORD) entry to. I doubt that the 'Procedural Option' is your problem. I've never heard of such an option, and I can't imagine why anybody would install Oracle without PL/SQL, or why that would even be an option. When I searched for the phrase, the first hit I found in the official documentation implies that this option was removed over 20 years ago, in version.
Prerequiste for Installation:
- Download the Oracle Database 12c installer package.
- The Swap Space size should be 16GB .
- Enable X11 Forwarding to “yes” in sshd configuration file.
- Properly set the hostname.
- Set the Kernel Parameters.
- Set the ulimit values.
- Install the required rpm packages.
1] OS Release
[root@quickfixlinux ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release
Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server release 7.5 (Maipo)
1.1] Set the Hostname :
(a) Under /etc/hosts:
192.168.xx.xx quickfixlinux.com
(b) Under /etc/hostname:
quickfixlinux.com
1.2] Set the SELINUX to “Permissive”
[root@quickfixlinux ~]#getenforce
Enforcing
[root@quickfixlinux ~]#setenforce 0
[root@quickfixlinux ~]# getenforce
Permissive
1.3] Install the required rpm packages:
[root@quickfixlinux ~]# yum install -y binutils compat-libstdc++-33 compat-libstdc++-33.i686 gcc gcc-c++ glibc glibc.i686 glibc-devel glibc-devel.i686 ksh libgcc libgcc.i686 libstdc++ libstdc++.i686 libstdc++-devel libstdc++-devel.i686 libaio libaio.i686 libaio-devel libaio-devel.i686 libXext libXext.i686 libXtst libXtst.i686 libX11 libX11.i686 libXau libXau.i686 libxcb libxcb.i686 libXi libXi.i686 make sysstat unixODBC unixODBC-devel zlib-devel
1.4] Set the limits for Oracle user in /etc/security/limits.conf file :
oracle soft nproc 131072
oracle hard nproc 131072
oracle soft nofile 131072
oracle hard nofile 131072
oracle soft core unlimited
oracle hard core unlimited
oracle soft memlock 50000000
oracle hard memlock 50000000
1.5] Set the Kernel Parameters:
[root@quickfixlinux ~]#/sbin/sysctl -w kernel.sem=”250 32000 100 128″
kernel.sem = 250 32000 100 128
[root@quickfixlinux ~]# /sbin/sysctl -w fs.aio-max-nr=1048576
fs.aio-max-nr = 1048576
[root@quickfixlinux ~]# /sbin/sysctl -w kernel.shmmax=4398046511104
kernel.shmmax = 4398046511104
[root@quickfixlinux ~]# /sbin/sysctl -w kernel.shmall=1073741824
kernel.shmall = 1073741824
[root@quickfixlinux ~]# /sbin/sysctl -w net.core.wmem_max=1048586
net.core.wmem_max = 1048586
[root@quickfixlinux ~]# /sbin/sysctl -w net.core.wmem_default=262144
net.core.wmem_default = 262144
[root@quickfixlinux ~]#/sbin/sysctl -w net.core.rmem_max=4194304
net.core.rmem_max = 4194304
[root@quickfixlinux ~]#/sbin/sysctl -w net.core.rmem_default=262144
net.core.rmem_default = 262144
[root@quickfixlinux ~]#/sbin/sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range=”9000 65500″
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 9000 65500
[root@quickfixlinux ~]# /sbin/sysctl -w kernel.shmmni=4096
kernel.shmmni = 4096
[root@quickfixlinux ~]# /sbin/sysctl -w kernel.shmmax=8329226240
kernel.shmmax = 8329226240
[root@quickfixlinux ~]# sysctl -p
[root@quickfixlinux ~]#sysctl -a
1.6] Set the DISPLAY Environment:
Now, as a root user:
(a) Make sure you have “Tick” the Enable X11 forwarding in PUTTY.
(b) Launch the “Xming” application from your local machine.
(c) touch /root/.Xauthority
(d) uncomment the X11Forwarding and set to “yes” in /etc/ssh/sshd_config file.
(e) [root@quickfixlinux ~]# xauth list $DISPLAY
localhost.localdomain/unix:10 MIT-MAGIC-COOKIE-1 3a49e090537be8161b19526143ff2988
(f)[root@quickfixlinux ~]#echo $DISPLAY
[ IF the output shows nothing, set the display env first… ]
(e)[root@quickfixlinux ~]#export DISPLAY= localhost:10.0
[root@quickfixlinux ~]# echo $DISPLAY
localhost:10.0
Now, as a oracle user:
(a) [oracle@quickfixlinux ~]$ touch .Xauthority
(b) [oracle@quickfixlinux ~]$ xauth list $DISPLAY
(c) [oracle@quickfixlinux ~]$ echo $DISPLAY
[ Both the xauth list and DISPLAY shows NO output, Whereas, we need to add it now. ]
(d) [oracle@quickfixlinux ~]$ xauth add localhost.localdomain/unix:10 MIT-MAGIC-COOKIE-1 3a49e090537be8161b19526143ff2988
[Add the root MIT-MAGIC-COOKIE in oracle user ]
(e) [oracle@quickfixlinux ~]$export DISPLAY= localhost:10.0
Now, try to issue the command “xclock” and wait for it launch.
2] Create user and groups:
[root@quickfixlinux ~]# useradd oracle
[root@quickfixlinux ~]# password oracle
[root@quickfixlinux ~]#groupadd oinstall
[root@quickfixlinux ~]#usermod -G oinstall oracle
2.2] Create the folders:
[root@quickfixlinux ~]# mkdir /oracle
[root@quickfixlinux ~]# chown -R oracle:oinstall /oracle
[root@quickfixlinux ~]# chmod -R 775 /oracle
[root@quickfixlinux ~]# chmod g+s /oracle
If you didn’t set the above kernel parameters for ulimit values, you will be encountering errors while installation as below :
Lets get into the Oracle 12c database Installation now:
As a oracle user, get into the respective path to install :
[oracle@quickfixlinux ~]$cd /database/
[oracle@quickfixlinux database]$ ./runInstaller
Starting Oracle Universal Installer…
Checking Temp space: must be greater than 500 MB. Actual 393933 MB Passed
Checking swap space: must be greater than 150 MB. Actual 51199 MB Passed
Checking monitor: must be configured to display at least 256 colors. Actual 16777216 Passed
Preparing to launch Oracle Universal Installer from /tmp/OraInstall2018-04-25_11-03-07PM. Please wait …
[oracle@quickfixlinux database]$
[STEP-1]
[STEP-2]
[STEP-3]
[STEP-4]
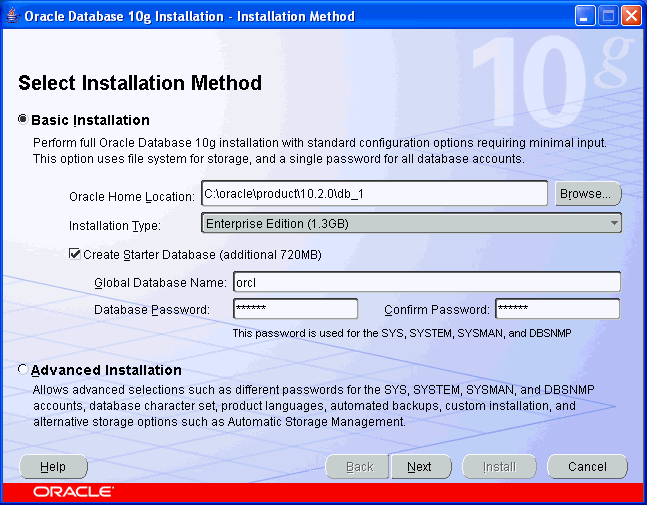
[STEP-5] There are two ways to do the installation, (1) Typical Install or (2) Advanced Install. Here, first we will look into (1) & then (2)
[STEP-6]
NOTE: password here can’t contain any special characters:
[STEP-7]
[STEP-8]
[STEP -5 – Advanced] Now, we will look on the Advanced Install options:
[STEP -6 – Advanced]
[STEP -7 – Advanced]
[STEP -8 – Advanced]
[STEP -9 – Advanced]
[STEP -10 – Advanced]
[STEP -11 – Advanced]
[STEP -12 – Advanced]
[STEP -13 – Advanced]
[STEP -14 – Advanced]
[STEP -15 – Advanced]
[STEP -16 – Advanced]
[STEP -17 – Advanced]
[STEP -18 – Advanced]
[STEP -19 – Advanced]
[STEP -20 – Advanced]
As a root user: Now, Change the /etc/oratab entry from “N” to “Y”
orcl:/oracle/app/oracle/product/12.2.0/dbhome_1:Y
As a Oracle user: Now, add the below Entries in .bash_profile file :
export ORACLE_HOSTNAME=quickfixlinux
export ORACLE_UNQNAME=orcl
export ORACLE_BASE=/u01/app/oracle
export ORACLE_HOME=$ORACLE_BASE/product/12.1.0/db_1
export ORACLE_SID=orcl
[oracle@quickfixlinux ~]$ source .bash_profile
[oracle@quickfixlinux ~]$ ./sqlplus
SQL*Plus: Release 12.2.0.1.0 Production on Thu Apr 26 01:46:19 2018
Copyright (c) 1982, 2016, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Enter user-name: SYS AS SYSDBA
Enter password: <password given while installation>
Connected to an idle instance.
To start the oracle LISTENER:
[oracle@quickfixlinux ~]$ lsnrctl status
LSNRCTL for Linux: Version 12.2.0.1.0 – Production on 03-MAY-2018 02:27:22
Copyright (c) 1991, 2016, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Connecting to (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=192.168.21.1)(PORT=1521)))
STATUS of the LISTENER
————————
Alias LISTENER
Version TNSLSNR for Linux: Version 12.2.0.1.0 – Production
Start Date 28-APR-2018 01:27:22
Uptime 5 days 0 hr. 59 min. 59 sec
Trace Level off
Security ON: Local OS Authentication
SNMP OFF
Listener Parameter File /oracle/app/oracle/product/12.2.0/dbhome_1/network/admin/listener.ora
Listener Log File /oracle/app/oracle/diag/tnslsnr/test123/listener/alert/log.xml
Listening Endpoints Summary…
(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=192.168.21.1)(PORT=1521)))
(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=ipc)(KEY=EXTPROCORCL)))
The listener supports no services
The command completed successfully
Resolution:
Edit the listener.ora file and change the HOST from IP ADDRESS to server hostname …
[oracle@quickfixlinux ~]$ vim /oracle/app/oracle/product/12.2.0/dbhome_1/network/admin/listener.ora
Complete this procedure to install Oracle Grid Infrastructure software for Oracle Domain Services Cluster.
Starting with Oracle Grid Infrastructure 12c Release 2 (12.2), the installation media is replaced with a zip file for the Oracle Grid Infrastructure installer. Run the installation wizard after extracting the zip file into the target home path.
At any time during installation, if you have a question about what you are being asked to do, or what input you are required to provide during installation, click the Help button on the installer page.
You should have your network information, storage information, and operating system users and groups available to you before you start installation, and you should be prepared to run root scripts.
As the user that owns the software for Oracle Grid Infrastructure for a cluster (grid) on the first node, install Oracle Grid Infrastructure for a cluster. Note that the installer uses Secure Shell (SSH) to copy the binary files from this node to the other nodes during the installation. During installation, in the Cluster Node Information window, when you specify the nodes in your cluster, you can click SSH Connectivity and the installer configures SSH connectivity between the specified nodes for you.
Note:
These installation instructions assume you do not already have any Oracle software installed on your system.To install the software for Oracle Domain Services Cluster:
- As the
griduser, download the Oracle Grid Infrastructure image files and extract the files into the Grid home. For example:grid.zipis the name of the Oracle Grid Infrastructure image zip file. For example, on Linux systems, the name of the Oracle Grid Infrastructure image zip file islinuxx64_12201_grid_home.zip.Note:
You must extract the zip image software into the directory where you want your Grid home to be located.
Download and copy the Oracle Grid Infrastructure image files to the local node only. During installation, the software is copied and installed on all other nodes in the cluster.
- Log in as the
griduser, and start the Oracle Grid Infrastructure installer by running the following command:The installer starts and the Select Configuration Option window appears. - Choose the option Configure Grid Infrastructure for a New Cluster, then click Next.
- Choose the option Configure an Oracle Domain Services Cluster, then click Next.The Grid Plug and Play Information window appears.
- In the Cluster Name and SCAN Name fields, enter the names for your cluster and cluster scan that are unique throughout your entire enterprise network.
You can select Configure GNS Hangouts plugin for outlook. if you have configured your domain name server (DNS) to send to the GNS virtual IP address name resolution requests for the subdomain GNS serves, as explained in this guide.
For cluster member node public and VIP network addresses, provide the information required depending on the kind of cluster you are configuring:
If you plan to use automatic cluster configuration with DHCP addresses configured and resolved through GNS, then you only need to provide the GNS VIP names as configured on your DNS.
If you plan to use manual cluster configuration, with fixed IP addresses configured and resolved on your DNS, then provide the SCAN names for the cluster, and the public names, and VIP names for each cluster member node. For example, you can choose a name that is based on the node names' common prefix. This example uses the cluster name
myclusterand the cluster SCAN name ofmycluster-scan.
The Cluster Node Information screen appears. - In the Public Hostname column of the table of cluster nodes, you should see your local node, for example
node1.example.com.The following is a list of additional information about node IP addresses:
For the local node only, OUI automatically fills in public and VIP fields. If your system uses vendor clusterware, then OUI may fill additional fields.
Host names and virtual host names are not domain-qualified. If you provide a domain in the address field during installation, then OUI removes the domain from the address.
Interfaces identified as private for private IP addresses should not be accessible as public interfaces. Using public interfaces for Cache Fusion can cause performance problems.
When you enter the public node name, use the primary host name of each node. In other words, use the name displayed by the
/bin/hostnamecommand.
- Click Add to add another node to the cluster.
- Enter the second node's public name (
node2), and virtual IP name (node2-vip), then click OK.You are returned to the Cluster Node Information window. You should now see all nodes listed in the table of cluster nodes. Make sure the Role column is set to HUB for both nodes. To add Leaf Nodes, you must configure GNS. - Make sure all nodes are selected, then click the SSH Connectivity button at the bottom of the window.The bottom panel of the window displays the SSH Connectivity information.
- Enter the operating system user name and password for the Oracle software owner (
grid). Select the option If you have configured SSH connectivity between the nodes, then select the Reuse private and public keys existing in user home option. Click Setup.A message window appears, indicating that it might take several minutes to configure SSH connectivity between the nodes. After a short period, another message window appears indicating that passwordless SSH connectivity has been established between the cluster nodes. Click OK to continue. - When returned to the Cluster Node Information window, click Next to continue.
- Select the usage type for each network interface displayed.Verify that each interface has the correct interface type associated with it. If you have network interfaces that should not be used by Oracle Clusterware, then set the network interface type to Do Not Use. For example, if you have only two network interfaces, then set the public interface to have a Use For value of Public and set the private network interface to have a Use For value of ASM & Private.Click Next. The Create ASM Disk Group window appears.
- Provide the name and specifications for the Oracle ASM disk group.
- In the Disk Group Name field, enter a name for the disk group, for example DATA.
- Choose the Redundancy level for this disk group. Normal is the recommended option.
- In the Add Disks section, choose the disks to add to this disk group.
When you have finished providing the information for the disk group, click Next.The Grid Infrastructure Management Repository Option window appears - Provide the name and specifications for the GIMR disk group.
- In the Disk Group Name field, enter a name for the disk group, for example
DATA1. - Choose the Redundancy level for this disk group. Normal is the recommended option.
- In the Add Disks section, choose the disks to add to this disk group.
- Select the Configure Rapid Home Provisioning Server option to configure a Rapid Home Provisioning Server as part of the Oracle Domain Services Cluster. Rapid Home Provisioning enables you to install clusters, and provision, patch, and upgrade Oracle Grid Infrastructure and Oracle Database homes.
When you have finished providing the information for the disk group, click Next. - In the Disk Group Name field, enter a name for the disk group, for example
- Choose the same password for the Oracle ASM SYS and ASMSNMP account, or specify different passwords for each account, then click Next.The Failure Isolation Support window appears.
- Select the option Do not use Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI), then click Next.
- If you have Enterprise Manager Cloud Control installed in your enterprise, then choose the option Register with Enterprise Manager (EM) Cloud Control and provide the EM configuration information. If you do not have Enterprise Manager Cloud Control installed in your enterprise, then click Next to continue.You can manage Oracle Grid Infrastructure and Oracle Automatic Storage Management (Oracle ASM) using Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control. To register the Oracle Grid Infrastructure cluster with Oracle Enterprise Manager, ensure that Oracle Management Agent is installed and running on all nodes of the cluster.The Privileged Operating System Groups window appears.
- Accept the default operating system group names for Oracle ASM administration and click Next.
- Specify the directory to use for the Oracle base for the Oracle Grid Infrastructure installation, then click Next. The Oracle base directory must be different from the Oracle home directory.If you copied the Oracle Grid Infrastructure installation files into the Oracle Grid home directory as directed in Step 1, then the default location for the Oracle base directory should display as
/u01/app/grid.If you have not installed Oracle software previously on this computer, then the Create Inventory window appears. - Change the path for the inventory directory, if required. Then, click Next.If you are using the same directory names as the examples in this book, then it should show a value of
/u01/app/oraInventory. The group name for theoraInventorydirectory should showoinstall.The Root Script Execution Configuration window appears. - Select the option to Automatically run configuration scripts. Enter the credentials for the root user or a sudo account, then click Next.Alternatively, you can Run the scripts manually as the
rootuser at the end of the installation process when prompted by the installer. - If any of the checks have a status of Failed and are not Fixable, then you must manually correct these issues. After you have fixed the issue, you can click the Check Again button to have the installer recheck the requirement and update the status. Repeat as needed until all the checks have a status of Succeeded. Click Next.
The Summary window appears.
- Review the contents of the Summary window and then click Install. The installer displays a progress indicator enabling you to monitor the installation process.
- If you did not configure automation of the root scripts, then you are required to run certain scripts as the
rootuser, as specified in the Execute Configuration Scripts window appears. Do not click OK until you have run the scripts. Run the scripts on all nodes as directed, in the order shown.For example, on Oracle Linux you perform the following steps (note that for clarity, the examples show the current user, node and directory in the prompt):
As the
oracleuser onnode1, open a terminal window, and enter the following commands:Enter the password for the
rootuser, and then enter the following command to run the first script onnode1:After the
orainstRoot.shscript finishes onnode1, open another terminal window, and as theoracleuser, enter the following commands:Enter the password for the
rootuser, and then enter the following command to run the first script onnode2:After the
orainstRoot.shscript finishes onnode2, go to the terminal window you opened in part a of this step. As therootuser onnode1, enter the following commands to run the second script,root.sh:Press Enter at the prompt to accept the default value.
Note:
You must run the
root.shscript on the first node and wait for it to finish. f your cluster has three or more nodes, thenroot.shcan be run concurrently on all nodes but the first. Node numbers are assigned according to the order of runningroot.sh. If you want to create a particular node number assignment, then run the root scripts in the order of the node assignments you want to make, and wait for the script to finish running on each node before proceeding to run the script on the next node. However, Oracle system identifier, or SID, for your Oracle RAC databases, do not follow the node numbers.After the
root.shscript finishes onnode1, go to the terminal window you opened in part c of this step. As therootuser onnode2, enter the following commands:After the
root.shscript completes, return to the OUI window where the Installer prompted you to run theorainstRoot.shandroot.shscripts. Click OK.The software installation monitoring window reappears.
When you run
root.shduring Oracle Grid Infrastructure installation, the Trace File Analyzer (TFA) Collector is also installed in the directory.grid_home/tfa. - After
root.shruns on all the nodes, OUI runs Net Configuration Assistant (netca) and Cluster Verification Utility. These programs run without user intervention. - During the installation, Oracle Automatic Storage Management Configuration Assistant (
asmca) configures Oracle ASM for storage. - Continue monitoring the installation until the Finish window appears. Then click Close to complete the installation process and exit the installer.
Caution:
Option Oracle Download
After installation is complete, do not remove manually or run cron jobs that remove /tmp/.oracle or /var/tmp/.oracle directories or their files while Oracle software is running on the server. If you remove these files, then the Oracle software can encounter intermittent hangs. Oracle Clusterware installations can fail with the error:
CRS-0184: Cannot communicate with the CRS daemon.
Install Procedural Option Oracle Tutorial
After your Oracle Domain Services Cluster installation is complete, you can install Oracle Member Clusters for Oracle Databases and Oracle Member Clusters for Applications.
Install Procedural Option Oracle Sql
Parent topic:Installing Oracle Grid Infrastructure for a New Cluster